In the field of virology, the terms Herpes Zoster and Herpes Simplex often come up, but many people aren’t clear on what differentiates the two. Although they share a name and belong to the same family of viruses, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options are quite different. This article will clarify these distinctions, helping you to understand Herpes Zoster and Herpes Simplex.
What is Herpes Zoster?
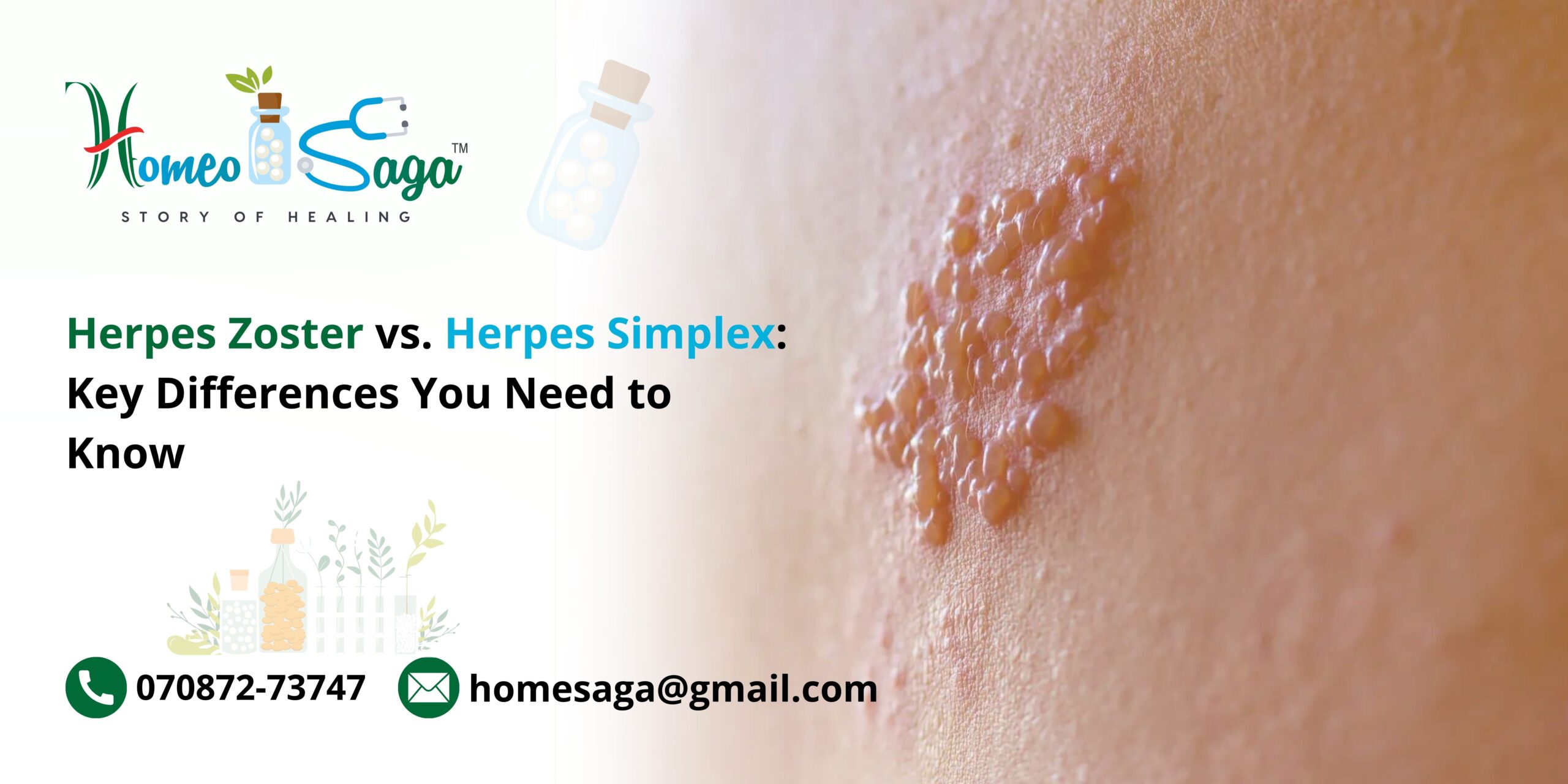
Herpes Zoster, commonly referred to as shingles, is caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). This is the same virus responsible for chickenpox. After someone has chickenpox, the virus can remain dormant in the nervous system and may reactivate later in life, especially in older adults or individuals with compromised immune systems.
Symptoms of Herpes Zoster
The symptoms associated with Herpes Zoster typically include:
- Initial Symptoms: A burning or tingling sensation may occur in a specific area before any visible rash appears.
- Rash Appearance: A painful rash usually develops on one side of the body, consisting of clusters of fluid-filled blisters.
- Accompanying Symptoms: Fever, fatigue, and general malaise can also manifest alongside the rash.
The pain from Herpes Zoster can be intense and may persist even after the rash resolves, leading to postherpetic neuralgia, a condition marked by chronic pain in the affected area.
What is Herpes Simplex?
Herpes Simplex encompasses two types of viruses: Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1) and Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 (HSV-2). HSV-1 is primarily associated with oral herpes, which results in cold sores, while HSV-2 is generally linked to genital herpes, causing sores in the genital region.
Symptoms of Herpes Simplex
Symptoms for Herpes Simplex can differ depending on the virus type:
- For HSV-1:
- Cold sores or fever blisters around the mouth
- Painful sores inside the mouth
- Swollen lymph nodes
- For HSV-2:
- Painful blisters in the genital area
- Itching or discomfort in the affected region
- Flu-like symptoms during the initial outbreak
Key Differences: Herpes Zoster vs. Herpes Simplex
Here are the main differences between Herpes Zoster and Herpes Simplex:
- Causative Virus:
- Herpes Zoster is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, while Herpes Simplex is caused by either HSV-1 or HSV-2.
- Symptom Manifestation:
- Herpes Zoster typically presents as a unilateral, painful rash localized to one side of the body, while Herpes Simplex results in sores that can occur on the lips (HSV-1) or in the genital area (HSV-2).
- Infection Type:
- Herpes Zoster is due to the reactivation of VZV from a past chickenpox infection. In contrast, Herpes Simplex can appear as either a primary infection or recurring outbreaks.
- Transmission:
- Herpes Zoster can be contagious, transmitting the varicella-zoster virus to individuals who have not had chickenpox. Herpes Simplex is spread mainly through direct contact with active sores.
- Treatment Options:
- Antiviral medications, such as acyclovir, are often prescribed for Herpes Zoster to alleviate symptoms. For Herpes Simplex, antiviral treatments are used to manage outbreaks and provide symptom relief.
Prevention Measures
Preventing both Herpes Zoster and Herpes Simplex is essential for public health. The shingles vaccine significantly reduces the risk of developing Herpes Zoster, particularly in older adults. To prevent Herpes Simplex, practicing safe sex, avoiding contact with active sores, and maintaining good hygiene are critical steps.
Conclusion
In summary, while Herpes Zoster and Herpes Simplex belong to the same family of viruses, they are fundamentally different in terms of their causes, symptoms, and treatment strategies. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective health management.
As you learn more about Herpes Zoster vs. Herpes Simplex, remember that seeking advice from a healthcare professional is vital if you suspect you have either condition. Knowledge is key to taking proactive steps in maintaining your health and well-being.